Life Science
Diffuse Optical Tomography (DOT) and Imaging (DOI)
Non-invasive techniques using near infrared light well suited for studying physiological tissue
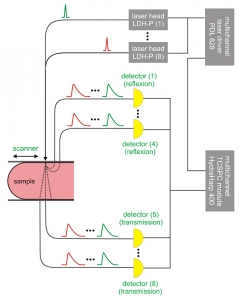
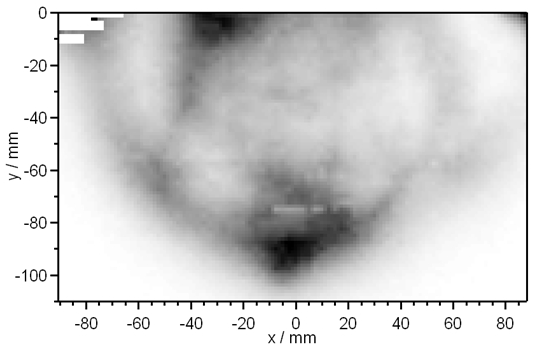
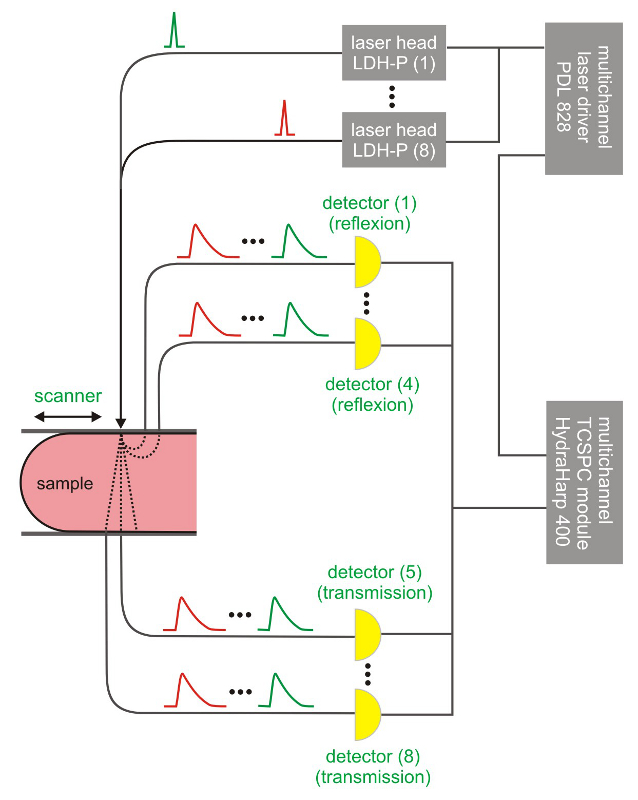
Diffuse Optical Tomography (DOT) and Imaging (DOI) are non-invasive techniques that utilize light in the near infrared spectral region to measure the optical properties of physiological tissue. The techniques rely on the object under study being at least partially light-transmitting or translucent, so it works best on soft tissues such as breast and brain tissue. By monitoring spatial-temporal variations in the light absorption and scattering properties of tissue, regional variations in oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin concentration as well as cellular scattering can be imaged. Based on these measurements, spatial maps of tissue properties such as total hemoglobin concentration, blood oxygen saturation and scattering can be obtained using model-based reconstruction algorithms. DOT and DOI have been applied in various deep-tissue applications including breast cancer imaging, brain functional imaging, stroke detection, muscle functional studies, photodynamic therapy, and radiation therapy monitoring.

 Contact us
Contact us